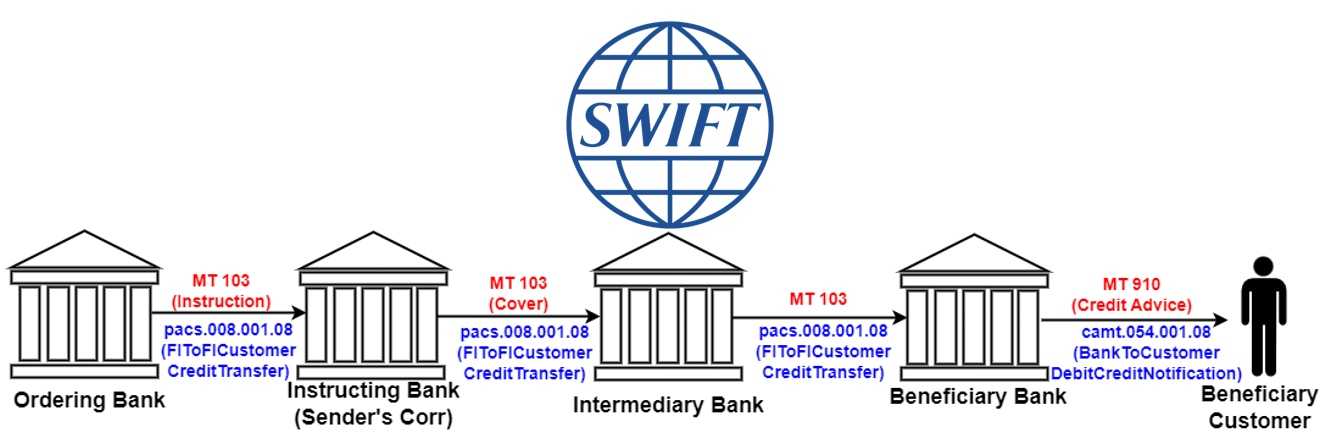
In the fast-paced world of international finance, the SWIFT network remains the backbone of secure and standardized communication between financial institutions. One of the most commonly used message types within the SWIFT ecosystem is the MT 103, also known as the Single Customer Credit Transfer.
Understanding MT 103
The MT 103 message is used by a financial institution to transfer funds from one account to another account held at a different institution. This message type is typically employed for customer transfers, where the ordering customer instructs their bank to credit the beneficiary customer’s account at another bank.
MT 103 Format and Field Details
The MT 103 message consists of several fields, each serving a specific purpose in facilitating the transfer request. Here’s a breakdown of the essential fields:
- Basic Header Block: This block includes fields such as the sender’s reference, message type, and destination details.
- Application Header Block: This section contains information about the message priority and delivery monitoring.
- User Header Block: This block encompasses fields related to the transfer type, value date, currency code, and exchange rate.
- Text Block: The text block carries the core information about the transfer, including the ordering customer’s details, beneficiary customer details, payment instructions, and remittance information.
- Trailer Block: The trailer block includes fields for authentication, such as the message authentication code.
Mapping MT 103 to MX
As the financial industry embraces modernization, SWIFT has introduced the ISO 20022 message format, known as MX (Message Transfer). The MX format aims to provide a more structured and standardized approach to financial messaging, facilitating easier processing and automation.
The corresponding MX message type for MT 103 is the pacs.008.001.08 (FIToFICustomerCreditTransfer). This MX message follows the XML format and includes elements that map to the fields found in the MT 103 message.
Below is the field by field mapping of tags in MT 103 with PACS elements, and also details of additional elements present in PACS 008 as per ISO 20022
| MT103 Tag | Description | PACS.008 Element | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| :20: | Transaction Reference Number | <TxRef> | Message Identification (Unique reference) |
| :23B: | Bank Operation Code | <LclInstrm> <Prtry> | Local Instrument (e.g., CRED for credit transfer) |
| :32A: | Value Date, Currency Code, Amount | <IntrBkSttlmAmt Ccy> <IntrBkSttlmDt> | Instructed Amount (Currency and Date) |
| :33B: | Currency/Instructed Amount | <IntrBkSttlmAmt Ccy> | Instructed Amount (Currency and Amount) |
| :50a: | Ordering Customer | <Dbtr> <DbtrAcct> | Debtor (Customer initiating the payment) and Debtor Account |
| :52A/C/D: | Ordering Institution | <DbtrAgt> | Debtor Agent (Financial Institution of the ordering customer) |
| :53A/B/D: | Sender’s Correspondent | <IntrmyAgt1> | Intermediary Agent 1 (Used if there’s an intermediary bank) |
| :54A/B/D: | Receiver’s Correspondent | <IntrmyAgt2> | Intermediary Agent 2 |
| :55A/B/D: | Third Reimbursement Institution | <IntrmyAgt3> | Intermediary Agent 3 |
| :56A/B/D: | Intermediary Institution | <IntrmyAgt> | Intermediary Agent |
| :57A/B/D: | Account with Institution | <CdtrAgt> | Creditor Agent (Financial Institution of the beneficiary) |
| :59: | Beneficiary Customer | <Cdtr> <CdtrAcct> | Creditor (Beneficiary) and Creditor Account |
| :70: | Remittance Information | <RmtInf> <Ustrd> | Unstructured Remittance Information |
| :71A: | Details of Charges | <ChrgsInf> <ChrgsAcct> | Charges Information and Charges Account |
| :72: | Sender to Receiver Information | <RmtInf> | Additional information or Instructions |
| :77B: | Regulatory Reporting | <RgltryRptg> | Regulatory Reporting (if applicable) |
Additional Elements in PACS.008
The PACS.008 message may include several additional elements not present in MT103:
| PACS.008 Element | Description | Equivalent in MT103 |
|---|---|---|
<CreDtTm> | Creation Date Time | No direct equivalent, this is the timestamp of message creation. |
<EndToEndId> | End-to-End Identification | Similar to Transaction Reference Number but more customer-oriented. |
<InstgAgt> | Instructing Agent | No direct equivalent, represents the party initiating the instruction. |
<InstdAgt> | Instructed Agent | No direct equivalent, represents the party receiving the instruction. |
While the field names and structures may differ, the MX format maintains the essence of the MT 103 message, ensuring a seamless transition and compatibility with modern financial messaging standards.
MT 103 Example
{1:F01BANKBEBBAXXX2222123456}{2:O1030906050514BANKDEFFXXXX22221234560505140906N}{3:{103:TGT}}{4:
:20:1234567890123456
:23B:CRED
:32A:051014EUR10000,
:50K:/1234567890
JOHN DOE
1 MAIN STREET
BRUSSELS BE
:52A:BNPAFRPPXXX
:59:/9876543210
JANE DOE
10 HIGH STREET
PARIS FR
:71A:SHA
:72:/INS/BNPAFRPPXXX
-}Mapping to MX pacs.008.001.08
<FIToFICstmrCdtTrf>
<GrpHdr>
<MsgId>1234567890123456</MsgId>
<CreDtTm>2023-08-22T12:30:00Z</CreDtTm>
</GrpHdr>
<CdtTrfTxInf>
<PmtId>
<InstrId>1234567890123456</InstrId>
<EndToEndId>1234567890123456</EndToEndId>
</PmtId>
<PmtTpInf>
<LclInstrm>
<Prtry>CRED</Prtry>
</LclInstrm>
</PmtTpInf>
<IntrBkSttlmAmt Ccy="EUR">10000</IntrBkSttlmAmt>
<IntrBkSttlmDt>2023-10-14</IntrBkSttlmDt>
<Dbtr>
<Nm>JOHN DOE</Nm>
<PstlAdr>
<StrtNm>1 MAIN STREET</StrtNm>
<TwnNm>BRUSSELS</TwnNm>
<Ctry>BE</Ctry>
</PstlAdr>
</Dbtr>
<DbtrAcct>
<Id>
<Othr>
<Id>1234567890</Id>
</Othr>
</Id>
</DbtrAcct>
<DbtrAgt>
<FinInstnId>
<BIC>BNPAFRPPXXX</BIC>
</FinInstnId>
</DbtrAgt>
<CdtrAgt>
<FinInstnId>
<BIC>BNPAFRPPXXX</BIC>
</FinInstnId>
</CdtrAgt>
<Cdtr>
<Nm>JANE DOE</Nm>
<PstlAdr>
<StrtNm>10 HIGH STREET</StrtNm>
<TwnNm>PARIS</TwnNm>
<Ctry>FR</Ctry>
</PstlAdr>
</Cdtr>
<CdtrAcct>
<Id>
<Othr>
<Id>9876543210</Id>
</Othr>
</Id>
</CdtrAcct>
<RmtInf>
<Ustrd>/INS/BNPAFRPPXXX</Ustrd>
</RmtInf>
<ChrgsInf>
<ChrgsAcct>SHA</ChrgsAcct>
</ChrgsInf>
</CdtTrfTxInf>
</FIToFICstmrCdtTrf>In this example, we have an MT 103 message with fields such as the sender’s reference, transfer type, value date, ordering customer details, beneficiary customer details, payment instructions, remittance information, and correspondent details. The corresponding MX pacs.008.001.08 message maps these fields to their respective XML elements, ensuring a seamless transition to the ISO 20022 standard.
As financial institutions continue to adopt the ISO 20022 standards, understanding the mapping between traditional SWIFT message types like MT 103 and their corresponding MX formats becomes increasingly important. By mastering this mapping, organizations can streamline their financial messaging processes, enhance efficiency, and maintain compliance with industry standards.